Microsoft Defender for cloud Series, Part 2 - How to provide better detection, investigation and response over all Defender for cloud solutions?
Introduction
As a security Architect, after answering the first question "Which defender for cloud plans should be enabled and why", mostly this question follows "How get a easier overview of detection, investigation and response over all Defender for cloud solutions?". To get a better understanding, in all the plans, I've wrote this blog, to give more clearance. This information can be found at Microsoft Learn.
What is Microsoft XDR?
Microsoft XDR (Extended Detection and Response) is a unified security solution that brings together multiple Microsoft security products to provide comprehensive, integrated, and automated protection across an organization’s entire digital infrastructure. The goal of XDR is to provide better detection, investigation, and response to threats by connecting data from different security systems (such as endpoints, email, identity, cloud services, and networks) into a central security framework.
XDR is designed to move beyond traditional security solutions by using advanced analytics, machine learning, and automation to offer more complete visibility and control across your environment. Microsoft’s XDR solution integrates with its broader security portfolio, such as Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, Microsoft Sentinel, Defender for Identity, and Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
Key Features of Microsoft XDR:
- Unified Threat Detection:
Microsoft XDR consolidates alerts and detections from various Microsoft Defender solutions and correlates them to provide deeper insights into security threats across multiple domains. Defender for Cloud focuses on securing cloud resources such as Azure VMs, containers, databases, and networks by providing visibility, threat protection, and compliance monitoring. Defender for Cloud XDR extends this capability by integrating with your broader security ecosystem, such as endpoints, identity services, and on-premises infrastructure. This allows the detection of cross-platform attacks and security incidents across the entire attack surface (both cloud and on-premises environments). - Comprehensive Visibility:
It offers visibility into threat activity by correlating security alerts across an organization’s entire digital estate, including endpoints, identity, cloud, and network. This integration allows security teams to have a centralized place for investigation. Defender for Cloud XDR consolidates security alerts from Defender for Cloud and other integrated solutions to make it easier to understand and respond to incidents. - Centralized Security Dashboard:
XDR centralizes all your security events and alerts into one place, simplifying security operations and investigations. The integration provides a unified view for security teams, merging Defender for Cloud security posture management with Defender for Cloud XDR threat detection. This combined dashboard helps track your security posture in real-time, offering a comprehensive analysis of your cloud and hybrid workloads. - Automated Response:
With XDR, automated playbooks and response actions can be triggered based on detected threats, reducing the time between detection and mitigation. It also allows you to customize responses based on the severity or type of threat, streamlining your incident response process. - Advanced Analytics:
It uses AI, machine learning, and behavioral analytics to improve detection accuracy and reduce false positives. By combining this data with Defender for Cloud’s telemetry, it can improve threat detection and identify sophisticated attack techniques that span across both cloud and on-premises environments. - Simplified Management:
It helps reduce complexity in managing multiple security tools. Instead of using separate solutions for endpoint protection, identity management, and cloud security, you get a unified approach that delivers better insights, faster response times, and fewer siloed tools. It’s also easier to configure and monitor policies across all your environments from a central place. - Better Threat Intelligence Sharing:
Defender for Cloud XDR integrates threat intelligence from various sources, including Microsoft Threat Intelligence, third-party providers, and internal telemetry from Defender solutions. It provides richer context around threats to help security teams identify new and emerging attack techniques that may target both cloud and on-premises systems. - Response to Hybrid Cloud Environments:
Defender for Cloud XDR is built to support hybrid environments, meaning you can manage and secure both on-premises and cloud-based infrastructure seamlessly. This hybrid approach ensures that organizations with multi-cloud or hybrid deployments have consistent visibility and protection across all their systems.
How to Integrate Microsoft XDR
Microsoft XDR works by integrating multiple security tools across an organization’s infrastructure. Here’s how you can integrate various Microsoft solutions to build an XDR environment:
1. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Integration
- Defender for Endpoint is a key component of Microsoft XDR and focuses on endpoint security. By integrating Defender for Endpoint with Microsoft XDR, you can gain advanced threat protection on endpoints, detect attacks in real-time, and respond quickly.
- Integration Steps:
- Enable Defender for Endpoint on your devices (Windows, macOS, Linux, etc.).
- Connect Defender for Endpoint to Microsoft Sentinel or Microsoft 365 Defender for enhanced visibility and correlation of alerts across endpoints and other domains (identity, email, etc.).
- Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint’s machine learning and behavioral analytics to improve threat detection.
2. Microsoft Sentinel (SIEM) Integration
- Microsoft Sentinel acts as a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system that aggregates security data from multiple sources, including Defender for Cloud, Defender for Identity, and Defender for Endpoint. Sentinel enhances XDR capabilities by providing advanced analytics and customized query capabilities for detecting threats across your entire infrastructure.
- Integration Steps:
- Set up Microsoft Sentinel and configure data connectors for various Microsoft Defender products, such as Defender for Endpoint and Defender for Identity.
- Send security logs and alerts from your Defender solutions to Sentinel to correlate data and get a broader view of your security landscape.
- Use Sentinel’s built-in workbooks, playbooks, and hunting queries for advanced threat detection and automated response.
3. Defender for Identity Integration
- Defender for Identity (formerly Azure Advanced Threat Protection) integrates with Microsoft XDR to detect identity-related threats such as credential theft, lateral movement, and privilege escalation.
- Integration Steps:
- Enable Defender for Identity on your on-premises Active Directory and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
- Integrate Defender for Identity with Microsoft Sentinel or Microsoft Defender for Identity to centralize detection and response for identity-based attacks.
- Leverage insights from Defender for Identity within Sentinel or Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to improve overall detection and threat response.
4. Defender for Office 365 Integration
- Defender for Office 365 is designed to protect your Office 365 environment against email threats such as phishing, malware, and business email compromise. Integrating Defender for Office 365 into the Microsoft XDR environment allows for correlation of email threats with other security data from endpoints, identity, and cloud resources.
- Integration Steps:
- Configure Defender for Office 365 within your Microsoft 365 security portal.
- Integrate Defender for Office 365 with Microsoft Sentinel for visibility into email threats across your organization.
- Set up automated playbooks and response actions in Sentinel based on email-related alerts.
5. Defender for Cloud Integration
- Defender for Cloud is Microsoft’s cloud security posture management (CSPM) and cloud workload protection platform (CWPP). It provides security for cloud services, including Azure, AWS, and GCP environments.
- Integration Steps:
- Integrate Defender for Cloud with Microsoft Sentinel to get security alerts related to cloud infrastructure, configurations, and workloads.
- Use Defender for Cloud’s security recommendations and alerts in conjunction with other XDR components for improved cloud security visibility.
- If using Defender for Cloud XDR, enable extended protection and advanced threat detection across both on-premises and cloud environments.
6. Automated Response and Playbooks
- Playbooks are a critical component in Microsoft XDR, enabling automated response to threats detected across various security products.
- Integration Steps:
- Set up Azure Logic Apps to create automated workflows that respond to security alerts from Microsoft Sentinel.
- For example, when a threat is detected in Defender for Endpoint or Defender for Cloud, a playbook can automatically quarantine an endpoint or isolate an affected network segment.
7. Custom Integrations
- Microsoft XDR also supports integrations with third-party solutions, allowing you to pull in additional security data (e.g., firewalls, VPNs, third-party SIEMs) and improve detection and response capabilities.
- Integration Steps:
- Use Microsoft Sentinel’s connectors to integrate third-party data sources.
- Correlate the data from these sources with Microsoft security products for extended threat detection.
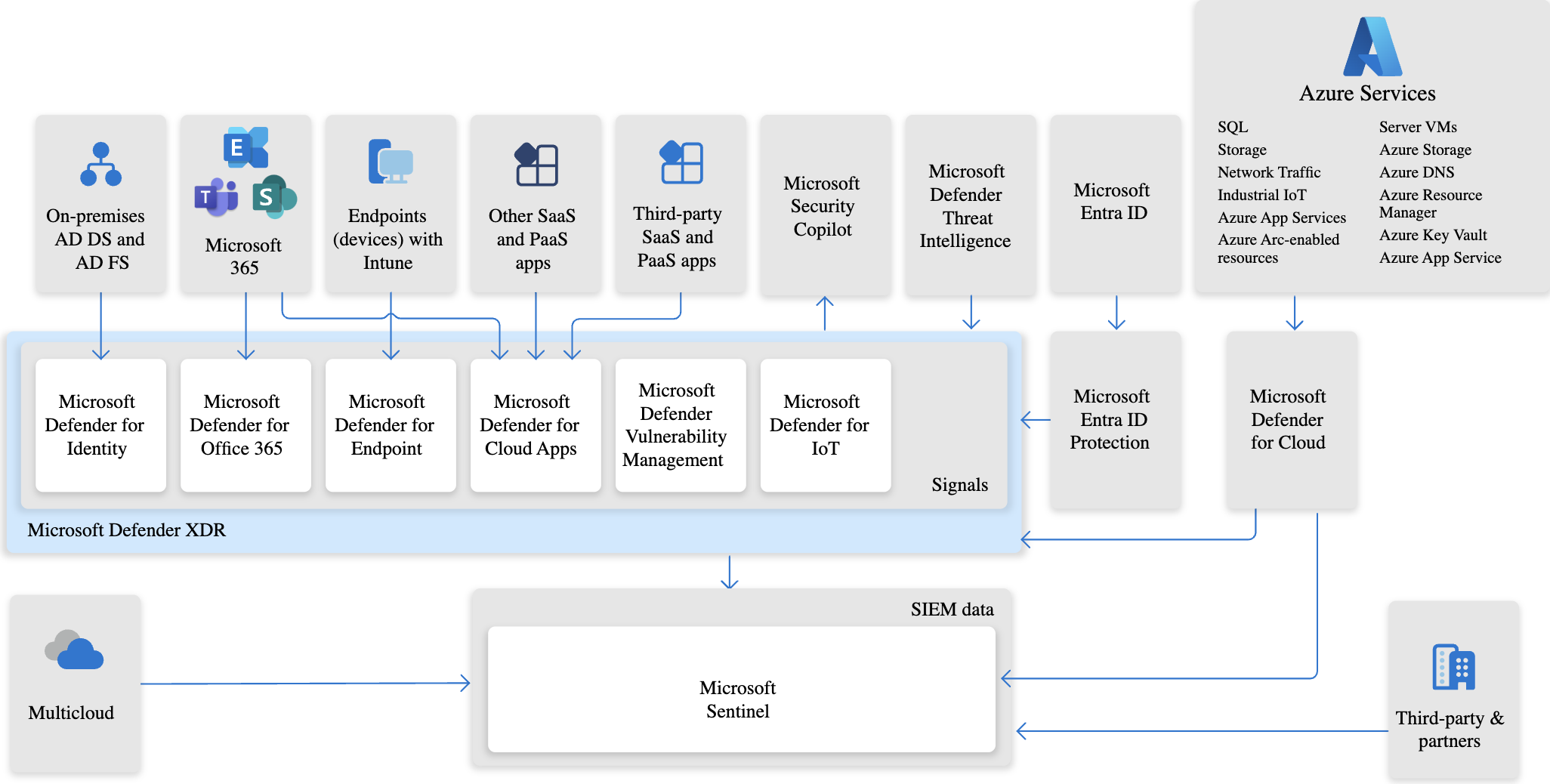
How to get started with XDR
To get started with Microsoft Defender for Cloud XDR (Extended Detection and Response), follow these steps to set up, configure, and integrate Defender for Cloud XDR with your existing security infrastructure:
1. Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have the following:
- Microsoft 365 Defender and Microsoft Defender for Cloud subscriptions.
- Azure subscription and appropriate permissions (Global Administrator or Security Administrator) to set up Defender for Cloud and XDR features.
- Access to Microsoft Sentinel (optional but recommended for a more comprehensive security view).
2. Enable Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is the foundation of the XDR capabilities in your cloud and hybrid environments. It provides security posture management and workload protection.
Sign in to Azure Portal:
- Go to the Azure portal.
- Ensure you have Global Administrator or Security Administrator access.
Set up Defender for Cloud:
- Navigate to Microsoft Defender for Cloud from the Azure portal.
- If this is your first time setting it up, select Get started to enable Defender for Cloud on your subscription.
- You’ll be prompted to select the resources you want to protect (Azure VMs, databases, storage, etc.).
Enable Security Plans:
- Under Environment Settings, enable the necessary security plans based on your workload needs. Defender for Cloud XDR integrates with a range of cloud resources such as Azure, AWS, and GCP, so enable these protections where applicable.
Enable Defender for Cloud XDR:
- Defender for Cloud XDR is often included with Defender for Cloud’s Cloud Workload Protection (CWP) and Posture Management capabilities. Make sure you enable the Cloud Workload Protection feature if you haven't done so already.
3. Integrate Defender for Endpoint (If Applicable)
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is an essential part of Defender for Cloud XDR, especially for endpoint security. Integrating it ensures protection for your devices and enables cross-platform threat detection.
Set up Defender for Endpoint:
- Navigate to the Microsoft 365 Defender portal.
- Go to Endpoint security and select Onboarding.
- Follow the onboarding steps for the devices you want to protect (Windows, macOS, Linux, etc.).
Integration with Defender for Cloud:
- In the Defender for Cloud portal, ensure that Defender for Endpoint is integrated. This integration will send endpoint alerts and incidents to the Defender for Cloud dashboard.
- The integration allows Defender for Cloud XDR to correlate alerts from endpoints, cloud workloads, and other sources to improve detection and response.
4. Integrate with Microsoft Sentinel (Optional but Recommended)
Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud-native SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) that can centralize and correlate alerts from Defender for Cloud XDR and other sources. This is an essential step to enhance your XDR capabilities.
Set up Sentinel:
- In the Azure portal, search for Microsoft Sentinel and create a new workspace or use an existing one.
- Follow the instructions to link Sentinel with your Defender for Cloud and other Microsoft Defender products.
Enable Data Connectors:
- Go to Configuration > Data connectors in the Sentinel workspace.
- Connect Defender for Cloud, Defender for Endpoint, Defender for Identity, and any other Microsoft security products to Microsoft Sentinel.
- This will allow Sentinel to ingest alerts and provide you with centralized security insights.
5. Configure Security Policies in Defender for Cloud
With Defender for Cloud enabled, configure security policies that align with your environment. These policies will set the foundation for threat detection across your cloud infrastructure and hybrid workloads.
Create and Assign Policies:
- Navigate to Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
- Under Environment settings, select Security policy and choose the policy type (e.g., Regulatory compliance, Cloud security posture, etc.).
- Define the severity of issues you want to monitor and enforce.
- These policies help identify vulnerabilities in your cloud resources and workloads and provide recommendations for security improvements.
6. Set Up Threat Detection and Alerts
Once Defender for Cloud and other products are integrated, set up alerting and threat detection mechanisms within the Defender for Cloud portal.
Configure Alerting:
- Go to Defender for Cloud > Alerts to configure how you want to receive notifications for security incidents.
- You can create custom alerts, set thresholds for specific severity levels, and integrate with Microsoft Sentinel for advanced alerting and response.
Monitor and Investigate Threats:
- Once everything is integrated, you can use Defender for Cloud’s XDR dashboard to monitor security incidents, view threat analytics, and investigate alerts.
- XDR will provide you with a comprehensive view of incidents and correlate them across endpoints, cloud, and hybrid environments.
7. Configure Automated Responses and Playbooks
To streamline your incident response, you can use Azure Logic Apps to create automated response playbooks that trigger actions when certain alerts are generated.
Create Playbooks in Sentinel:
- In Microsoft Sentinel, go to Playbooks and create a new playbook.
- Set up actions based on triggered alerts (e.g., isolating a VM, blocking a user, sending an email, etc.).
Test and Optimize Playbooks:
- Regularly test and refine your playbooks to ensure they are responding to the right events and providing the desired outcomes.
8. Review Security Posture and Recommendations
Defender for Cloud provides actionable security posture recommendations. Regularly review these suggestions and follow best practices for securing your cloud and hybrid environments.
Review Recommendations:
- Go to Defender for Cloud > Recommendations to view suggested improvements for your workloads, identities, and configurations.
- Implement these recommendations to further harden your environment against potential attacks.
9. Training and Awareness
- Train your security and IT teams on how to use Defender for Cloud XDR effectively, especially how to interpret alerts, investigate incidents, and use automated response playbooks.
- Stay updated on new features, integration options, and best practices via Microsoft’s official documentation and security webinars.
Conclusion:
In short, the integration between Defender for Cloud and Defender for Cloud XDR strengthens an organization’s security posture by offering advanced detection, automated responses, and a holistic view of threats across both cloud and hybrid environments. This integration streamlines security operations and improves visibility, helping teams prevent and respond to evolving security threats more efficiently.
To implement Microsoft XDR, you'll need to integrate various Microsoft Defender solutions, including Defender for Endpoint, Defender for Identity, Defender for Office 365, Defender for Cloud, and Microsoft Sentinel. By centralizing security data from multiple sources, correlating alerts, and using automation for response, Microsoft XDR provides a robust solution for detecting, investigating, and responding to modern cybersecurity threats across a wide range of environments.
To get started with Defender for Cloud XDR, you need to:
- Set up Defender for Cloud and Defender for Endpoint (if applicable).
- Integrate with Microsoft Sentinel for centralized monitoring and threat analytics.
- Configure policies, alerts, and automated responses to ensure your organization is well-protected against cloud and hybrid threats.
- Regularly review security posture and refine your XDR setup as needed.
By following these steps, you'll ensure that your organization has robust detection and response capabilities to handle emerging security threats across your infrastructure.